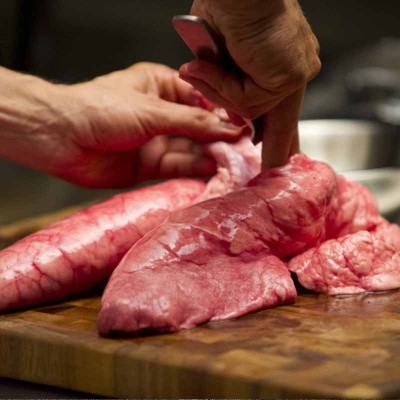
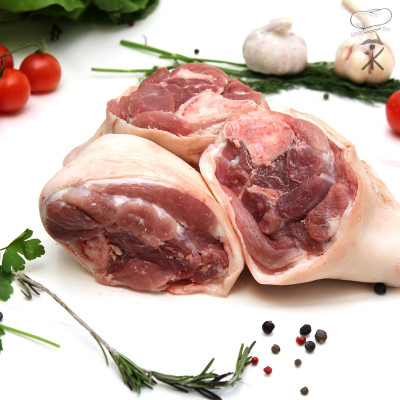
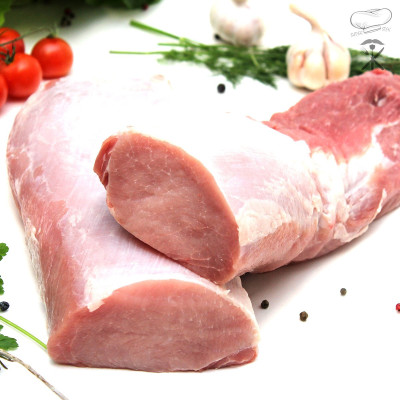
Płucka wołowe, czy wieprzowe są niedoceniane przez nas. Mogą być wspaniałym składnikiem farszów do pierogów, czy pasztecików.
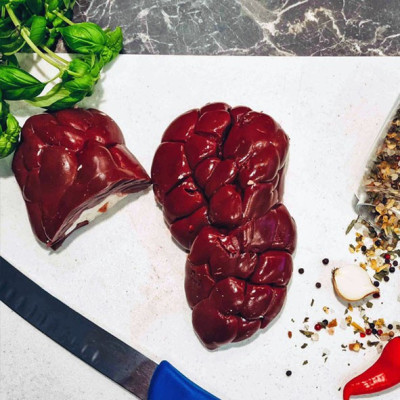
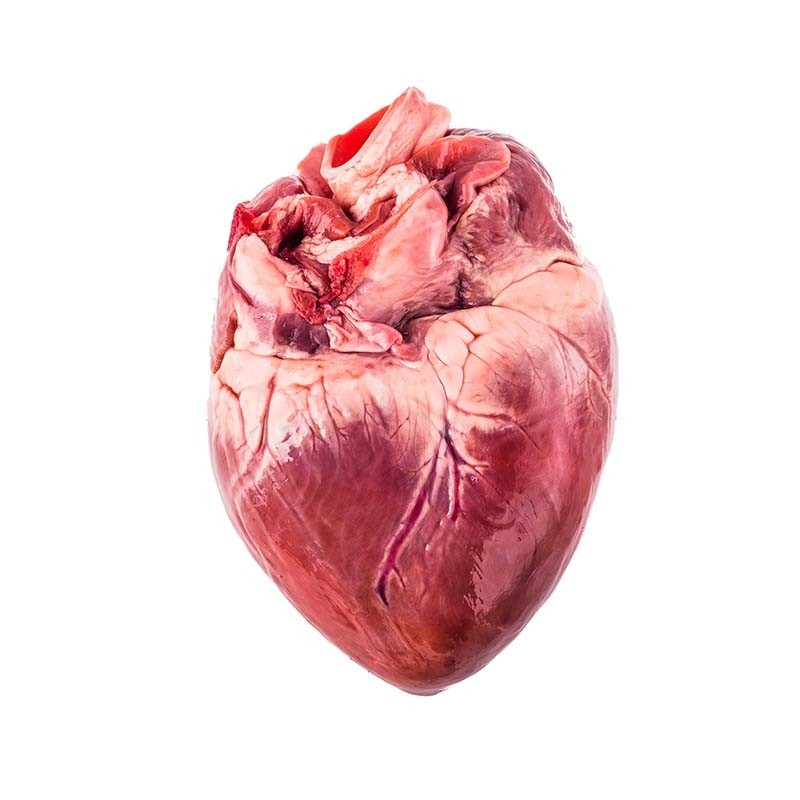
Pig hearts for learning anatomy, dissection, and research
(zł15.00 / kg)
Product customization
🧪 The use of pig hearts in science
Pig hearts are used in many fields of education and scientific research:
- Anatomy and physiology – learning about the structure of the heart, circulatory system, and valves
- Experimental surgery – practicing vessel suturing and cardiological procedures
- Forensic medicine and pathology – analyzing disease changes and performing autopsies
- Biological education – laboratory classes for students and medical school pupils
🔬 How to store pig hearts for educational purposes?
To ensure the best quality and preservation of anatomical structure, pig hearts should be stored under appropriate conditions:
- Refrigeration (0-4°C) – fresh hearts can be stored for up to 48 hours
- Freezing (-18°C) – longer storage without loss of structural quality
- Formalin preservation – for long-term display and pathomorphological studies
👉 Tip: If the hearts are to be used for dissection, it is best to thaw them slowly in the refrigerator for 12-24 hours to avoid tissue damage.
🏥 Frequently Asked Questions
• Are pig hearts an accurate representation of the human heart?
Yes, in terms of structure, pig hearts are anatomically similar to human hearts, making them often used in education and research.
• Can pig hearts be used for surgical training?
Yes, they are excellent material for practicing tissue suturing and experimental cardiological procedures.
• How long can hearts be stored for classes?
In refrigeration conditions up to 48 hours, and in the freezer even for several months.
• Can pig hearts be used in forensic medicine?
Yes, they are often used for learning heart pathology and analyzing disease changes.
✨ Summary
Pig hearts are an excellent anatomical model used in medical, veterinary, and biological education. Their realistic structure, availability, and ease of storage make them an indispensable tool for learning anatomy, surgery, and pathology. If you are looking for a natural model for dissection and educational classes, pig hearts will be an excellent choice! 🏥🔬